Transition Waivers: Which one is right for me?
- Sharon Starkey

- Mar 15, 2021
- 6 min read
Trying to understand and wade through waivers is confusing. This article will attempt to show the service differences between the transition waivers. We will be looking at the EBD waiver (Elderly, Blind, Disabled), the SLS waiver (Supported Living Services) and the DD waiver (Developmental Disability).
EBD waiver: The EBD waiver provides assistance to individuals who are 65 and older and have a functional impairment and individuals who are 18 and older who are physically disabled or require long-term supports and services in order to remain in a community setting.
SLS waiver: The SLS waiver provides necessary services and supports for individuals (18 and older) with intellectual or developmental disabilities so they can remain in their homes and communities.
DD waiver: The DD waiver provides access to 24/7 supervision/supports through Residential Habilitation and Day Habilitation Services. Living arrangements can range from host home to group home settings and residential supports for individuals who live with and/or are provided services by members of their family.
The SLS and DD waivers can be accessed through your local community centered board (CCB). The EBD waiver can be accessed through Single Entry Points (SEP) in your area.
Here is a basic chart comparing the services provided by each waiver:
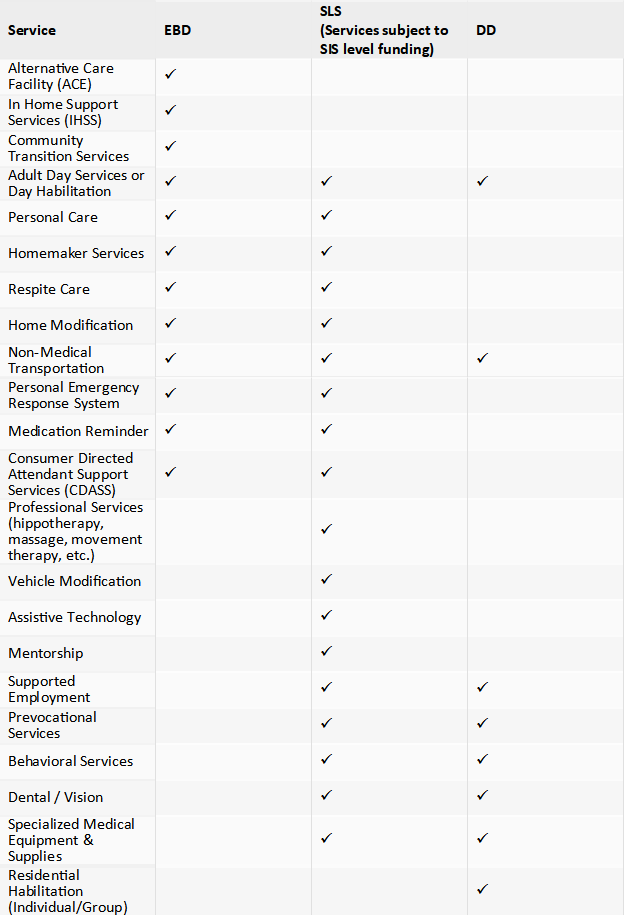
I would also like to highlight a few of the service definitions that I am often asked about by people inquiring about the difference in the waivers.
Personal Care
SLS: Personal Care is assistance to enable a client to accomplish tasks that the client would complete without assistance if the client did not have a disability. This assistance may take the form of hands-on assistance by actually performing a task for the client or cueing to prompt the client to perform a task.
EBD: Services which provide assistance to a client in their own home in order to meet the client's physical, maintenance and supportive needs. This assistance may take the form of hands-on assistance (actually performing a task for the person) or cueing to prompt the participant to perform a task. Personal care services do not require the supervision of a nurse or physician's orders.
Respite Care
SLS: Respite Care means services provided to an eligible client who is unable to care for himself/herself on a short-term basis because of the absence or the need for relief of those persons normally providing care. Respite Care is provided in the client’s residence and may be provided by different levels of providers depending upon the needs of the client.
EBD: Respite care services are provided to an eligible client on a short-term basis because of the absence or need for relief of those persons normally providing the care. Respite Care may be provided in a Class 1 nursing facility, an alternative care facility or by an employee of a certified personal care agency in the client's home. An individual client shall be authorized for no more than 30 days of respite in each calendar year.
Adult Day Services or Day Habilitation
SLS / DD: Day Habilitation Services and Supports include assistance with the acquisition, retention or improvement of self-help, socialization and adaptive skills that take place in a non-residential setting, separate from the client’s private residence or other residential living arrangement, except when services are necessary in the residence due to medical or safety needs. Day Habilitation Services and Supports encompass three (3) types of habilitative environments: 1) specialized habilitation services, 2) supported community connections, and 3) prevocational services.
EBD: Services furnished four or more hours per day in a community-based setting, encompassing both health and social services needed to ensure the optimal functioning of the participant.
Professional Services (hippotherapy, massage, movement therapy, etc.)
SLS: Professional services are provided by licensed, certified, registered or accredited professionals and the intervention is related to an identified medical or behavioral need.
Homemaker Services
SLS: Homemaker Services are provided in the client’s home and are allowed when the client’s disability creates a higher volume of household tasks or requires that household tasks are performed with greater frequency. There are two types of Homemaker Services: Basic Homemaker Services includes cleaning, completing laundry, completing basic household care or maintenance within the client’s primary residence only in the areas where the client frequents. Enhanced Homemaker Services include Basic Homemaker Services with the addition of either procedures for habilitation or procedures to perform extraordinary cleaning.
EBD: Homemaker Services are general household activities provided in the home of an eligible client, provided by a Homemaker Provider Agency to maintain a healthy and safe home environment for a client. When the person ordinarily responsible for these activities is absent or unable to manage these tasks. Covered benefits shall be for the benefit of the client and not for the benefit of other persons living in the home. Services shall be applied only to the permanent living space of the client.
Home Modifications
SLS: The total cost of home accessibility adaptations, vehicle modifications, and assistive technology shall not exceed $10,000 over the five (5) year life of the HCBS Waiver except that on a case-by-case basis the Operating Agency may approve a higher amount.
EBD: There is a $10,000 lifetime maximum for the home modification benefit.
Non-medical Transportation
SLS/DD: Non-Medical Transportation enables clients to gain access to Day Habilitation Services and Supports, Prevocational Services and Supported Employment services.
EBD: Non-medical transportation services shall include, but not be limited to, transportation between the client's home and nonmedical services or resources such as adult day services, shopping, therapeutic swimming, dentist appointments, counseling sessions, and other services as required by the care plan to prevent institutionalization
Vehicle Modification
SLS: Vehicle modifications are adaptations or alterations to an automobile or van that is the client’s primary means of transportation; to accommodate the special needs of the client; are necessary to enable the client to integrate more fully into the community; and to ensure the health and safety of the client.
Assistive Technology
SLS: Assistive Technology includes services, supports or devices that assist a client to increase maintain or improve functional capabilities. This may include assisting the client in the selection, acquisition, or use of an assistive technology device.
Mentorship
SLS: Mentorship Services means services provided by peers to promote self-advocacy and encourage community living among clients by instructing and advising on issues and topics related to community living, describing real-world experiences as example and modeling successful community living and problem-solving.
Supported Employment
SLS/DD: Integrated employment services (supported employment) provides individuals with considerable ongoing job-related services and supports to obtain and maintain paid work in a regular community work setting.
Prevocational Services
SLS/DD: Prevocational services are designed to assist individuals with developmental disabilities in acquiring and maintaining work habits and work-related skills. Prevocational services are intended to have a more generalized result as opposed to vocational training for a specific job.
Behavioral Services
SLS/DD: Behavioral Services are services related to a client’s developmental disability which assist a client to acquire or maintain appropriate interactions with others.
Dental / Vision
SLS/DD: Dental Services means dental services that are inclusive of diagnostic, preventive, periodontal and prosthodontic services, as well as basic restorative and oral surgery procedures to restore the client to functional dental health and not available through the Medicaid State Plan. Vision Services means services that include eye exams and diagnosis, glasses, contacts, and other medically necessary methods to improve specific vision system problems when not available through the Medicaid State Plan.
Specialized Medical Equipment & Supplies
SLS/DD: Specialized Medical Equipment and Supplies include: devices, controls, or appliances that are required due to the client’s disability and that enable the client to increase the client’s ability to perform activities of daily living or to safely remain in the home and community.
Residential Habilitation (Individual/Group)
DD: Under Residential Habilitation Services and Supports (RHSS) the responsibility for the living environment rests with the service agency and encompass two types of living environments: Individual Residential Services and Supports (IRSS) and Group Residential Services and Supports (GRSS).
The following activities are performed by staff and are designed to assist individuals to reside as interdependently as possible in the community:
Self-advocacy training may include training to assist in expressing personal preferences, self-representation, individual rights, and to make increasingly responsible choices.
Independent living training may include personal care, household services, child and infant care (for parents themselves who are developmentally disabled), and communication skills such as the telephone.
Cognitive services may include training involving money management and personal finances, planning and decision making.
Implementation of recommended follow-up counseling, behavioral or other therapeutic interventions by residential staff, under the direction of a professional, that are aimed at increasing the overall effective functioning of an individual.
Emergency assistance training includes developing responses in case of emergencies; prevention planning and training in the use of equipment or technologies used to access emergency response systems.
Community access services that explore community services available to all people, natural supports available to the individual, and develop methods to access additional services/supports/activities desired by the individual
Travel services may include providing, arranging, transporting, or accompanying a person with developmental Disabilities to services and supports identified in the Individualized Plan (plan of care).
Supervision services may include a person safeguarding an individual with developmental disabilities and/or utilizing technology for the same purpose.
IRSS can be provided through the Family Care Giver Option. This allows an individual to stay in their home and have a family member or non-related person become a paid provider to implement services.
In Home Support Services (IHSS)
EBD: In-Home Support Services (IHSS) is a participant-directed service option that enables participants to direct who is providing their care, as well as the type of care to be provided. IHSS enables consumers to decide which services to use, which workers to hire, and what time of day they will come.
Information courtesy of workshop attended by PASCO. For more information on PASCO, please visit https://pascohh.com/




